Assessment
History
- Past medical history and birth history
- Airway-related comorbidities
- Prior airway management/ complications during anesthesia
- Surgical procedures involving the airway.
Physical Exam
A focused airway exam:
- Evaluation of the mandible, maxilla, and tongue size
- Loose or missing teeth
- Gross anatomic abnormalities
- Thyromental Distance:
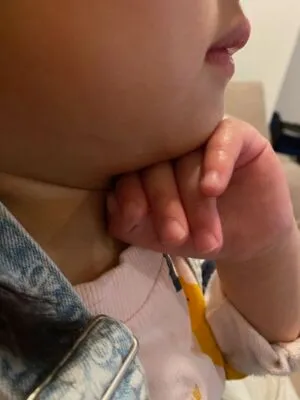
Appropriate thyromental distance varies with age and height. An alternate estimate is to evaluate if the distance between the mentum and the neck/mandible junction (near the hyoid bone) is equal to or greater than the width of 3 patient fingers.
Assessment of Airway Before Intubation
Alexander Connelly, Young May Cha. Pediatric Airway Evaluation [Internet]. 2024. Available from: https://www.openanesthesia.org/keywords/pediatric-airway-evaluation/
Assessing the Pediatric Airway Prior to Intubation by T. Miller [Internet]. Available from: https://youtu.be/UIvtoi2UZ-4?si=NZWLM9BGmEZCZFqn.
Equipment
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Mask
- Eye Protection
- Gown
- Gloves
Monitoring Equipment
- Pulse oximetry
- Non-invasive blood pressure monitoring (either automated or manual)
- Cardiac monitor
- End Tidal CO2 (ETCO2) or if unavailable use a colorimetric device
Airway Equipment
Airway Equipment Size Guide
- Endotracheal Tube (ETT)
Estimated endotracheal tube size
- CUFFED ETT = age / 4 + 3.5
UNCUFFED ETT = age / 4 + 4
- This formula yields the inside diameter of the tube in mm
- Always have an ETT half size smaller for back up
- Suction Device
- Rigid oral suction system (Yankaeur) with regulator set to maximum suction level

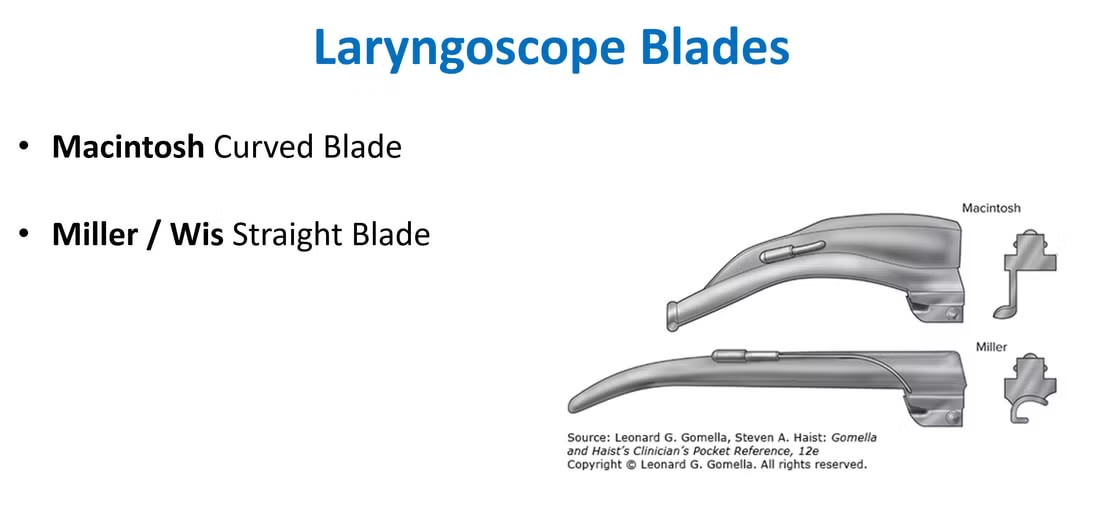
- Pediatric Laryngoscope
- The video laryngoscopes are preferred if there is a suitable blade size but may not be available in many centres
- The Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) checklist describes recommended laryngoscope sizes and blade types for patient age.
- For neonates and infants, a Miller/Robertshaw laryngoscope blade is recommended.
- For older children, the Macintosh blade is recommended.
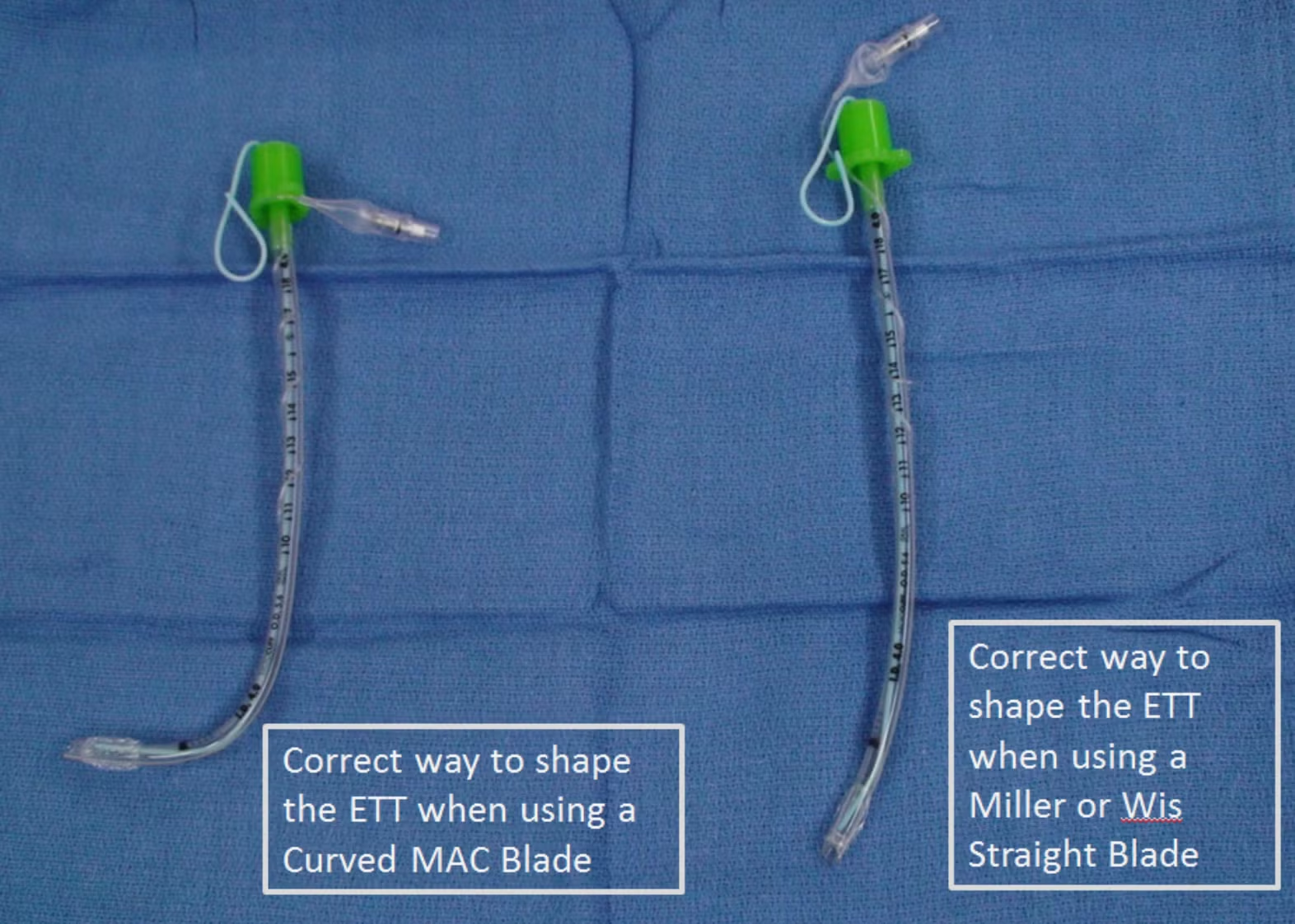
- Stylet
Semi-rigid stylet (for endotracheal tube), lubricated with any water based lubricating jelly.- Satin-slip stylet by Mallinckrodt is recommended if available.
- Stylet should be shaped to reflect a hockey stick prior to insertion.
5 mL Syringe
To inflate cuff with 1 to 2 mL air after successful intubation- Peripheral Intravenous (IV) Access
Ensure functioning IV access available
BCCH Pediatric Intensive Care Unit – Medical Director. INTUBATION IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS [Internet]. 2022. Available from: https://shop.healthcarebc.ca/phsa/BCWH_2/BC%20Children%27s%20Hospital/C-05-07-62873.pdf
Checklist
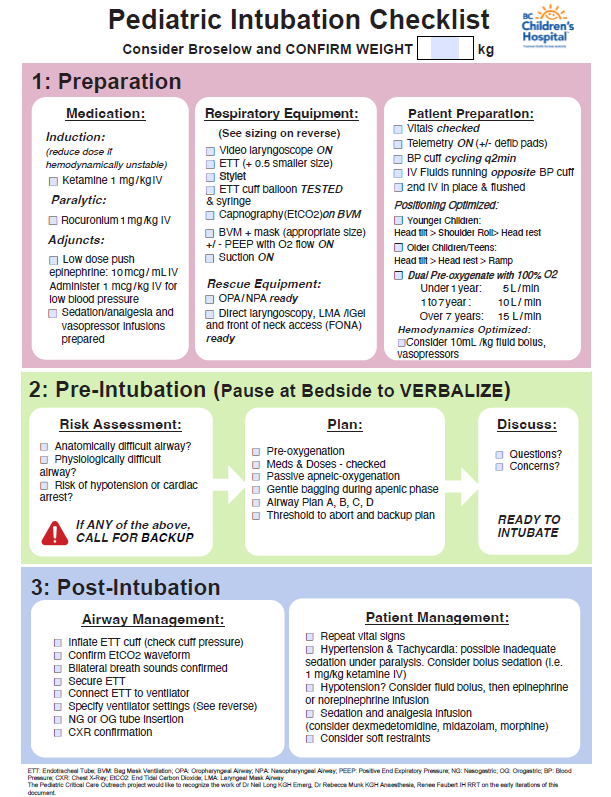
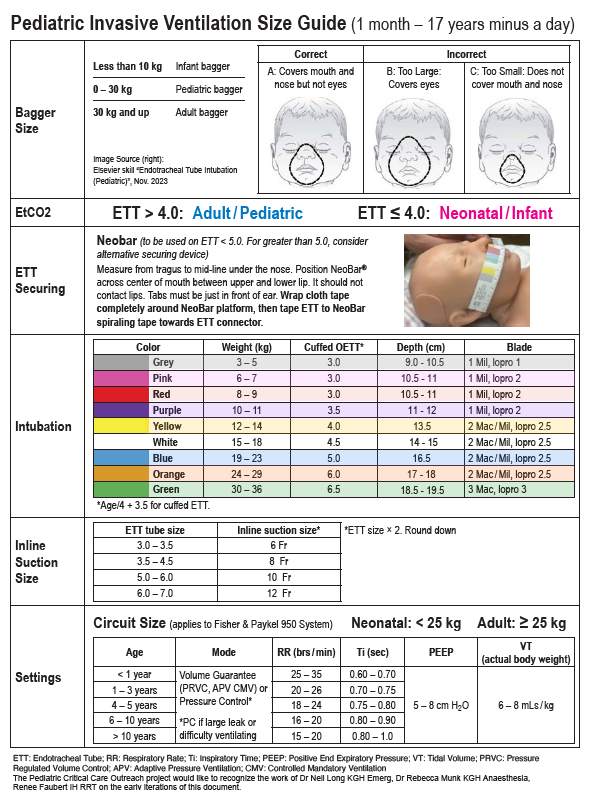
Long N, Munk R, Faubert R. Pediatric Intubation Checklist [Internet]. BC Children’s Hospital; Available from: https://www.childhealthbc.ca/media/1036
Preparation
- Positioning
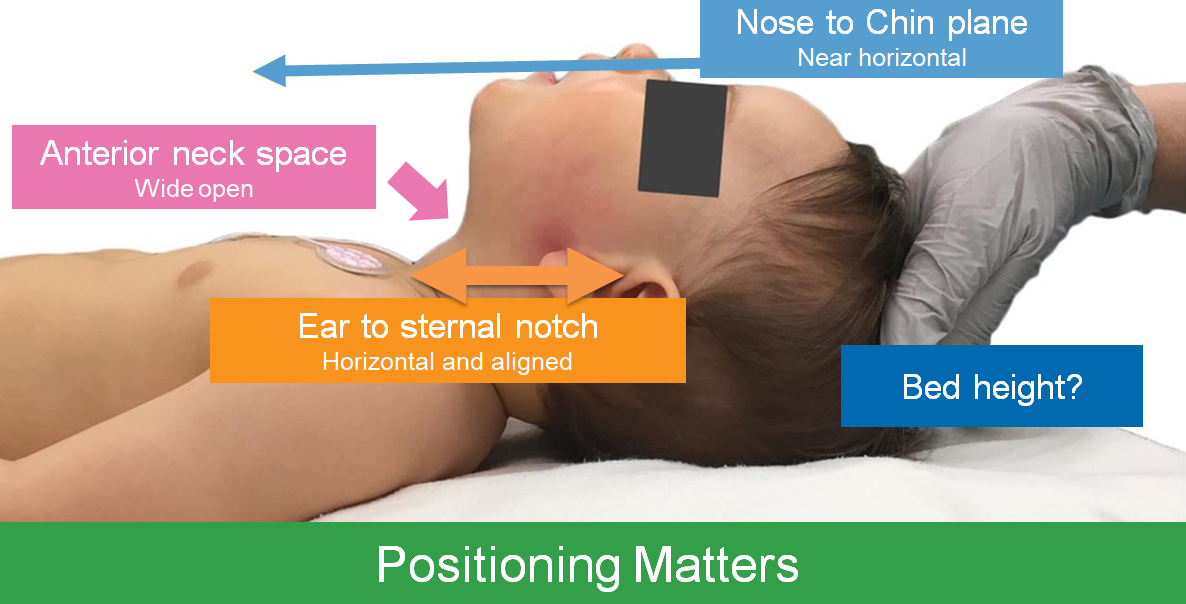
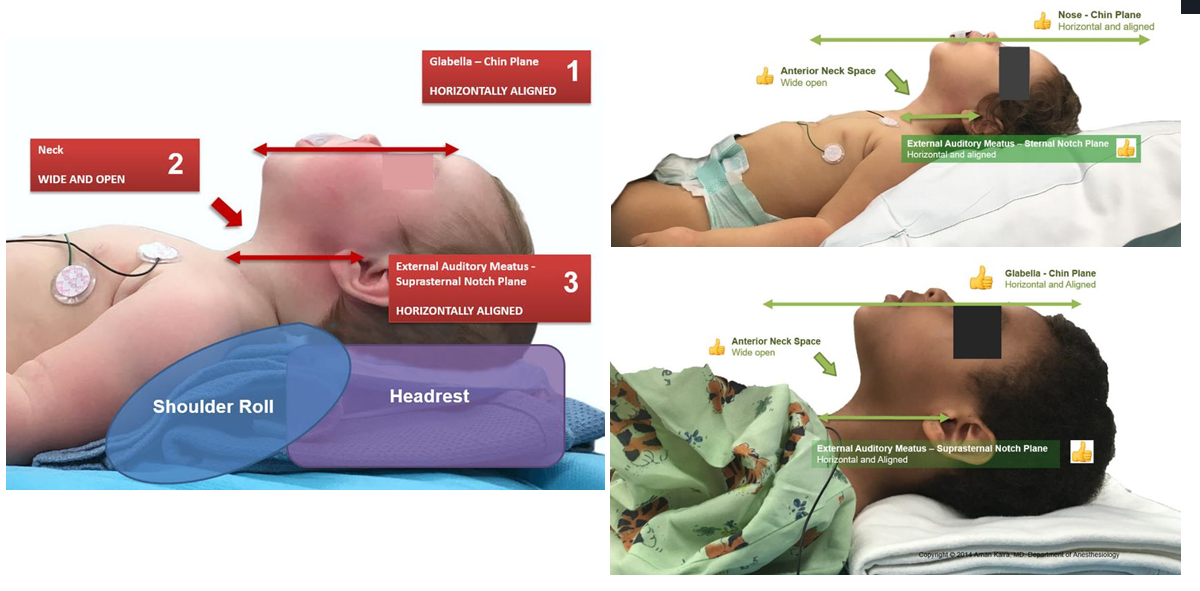
- Pre-Oxygenation
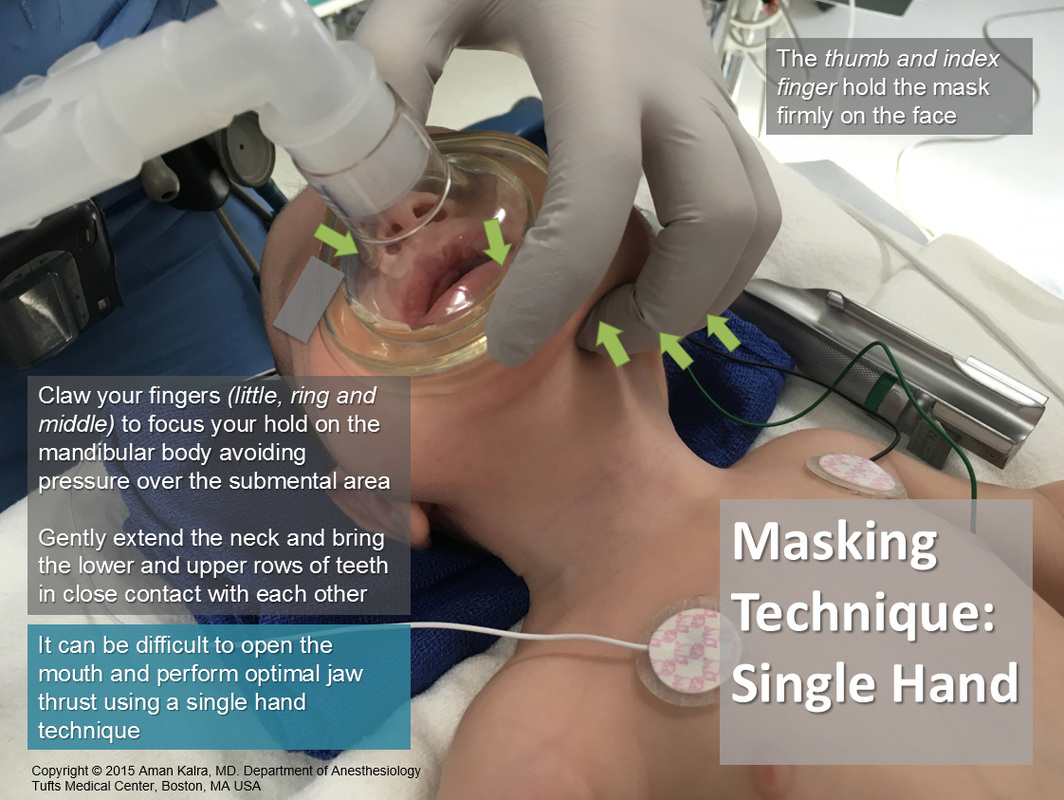
Prior to every intubation attempt, maintain with oxygen via nasal prongs ( <1 yr = 5LPM, 1-7 yr = 10LPM, > 7 yr = 15 LPM), in addition to 100% oxygen via bag-valve-mask (tight anatomical seal; see Figure below)
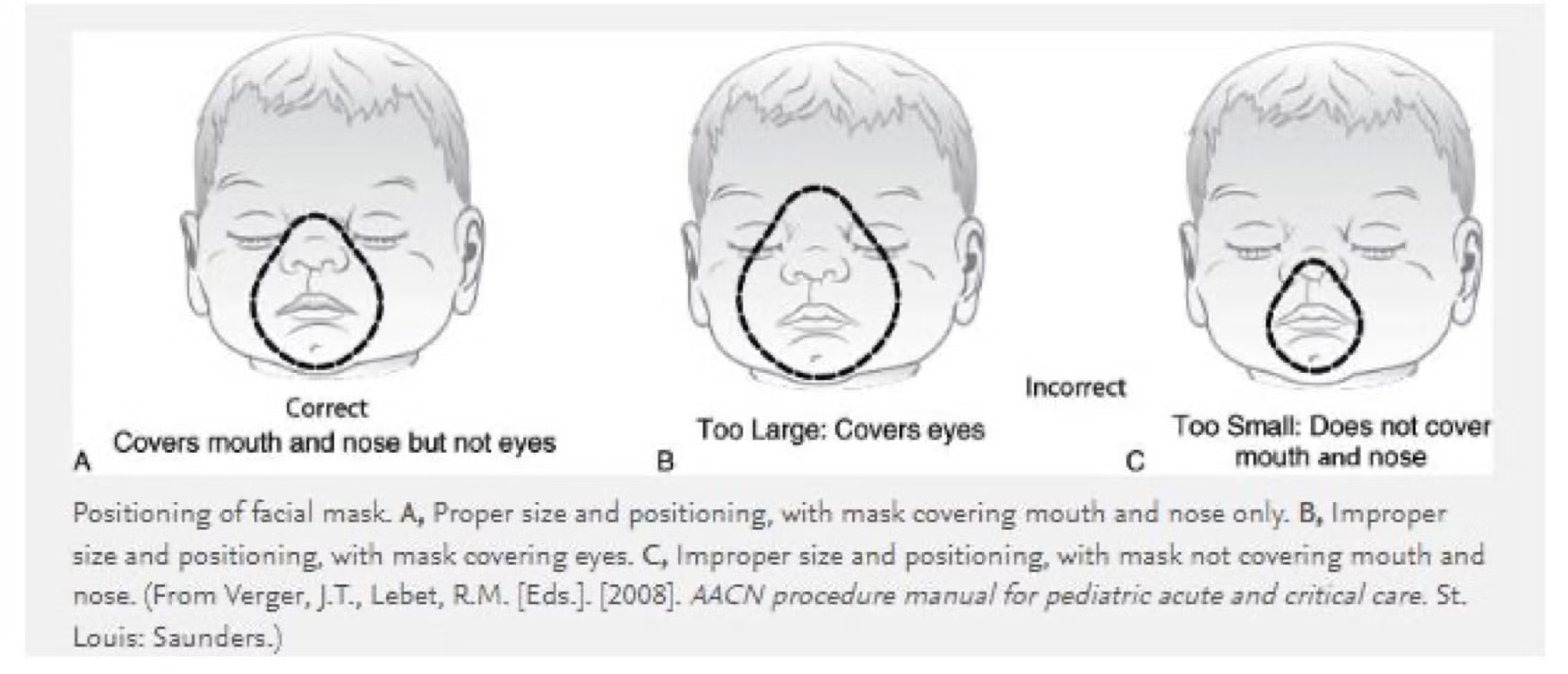
This should be maintained while preparing equipment and medications
If the face mask seal is impaired by the nasal prongs, remove the nasal prongs and optimize bag mask ventilation/oxygenation
Preventing Hypotension
Hypovolemia, sedative medications and positive pressure ventilation may result in hypotension during the intubation procedure.
- Fluid bolus ( isotonic crystalloid solution fluid bolus 10-20mL/kg IV)
- Inotropes/vasopressor
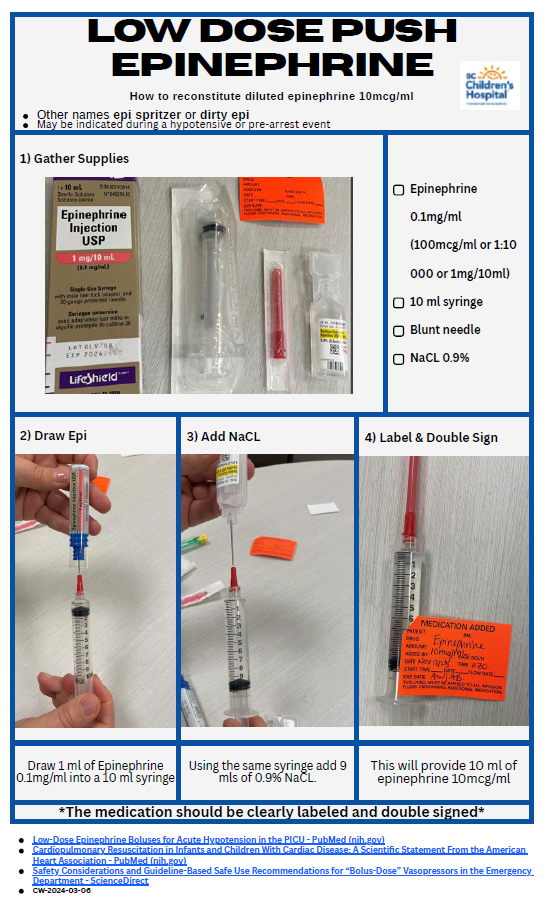
- Low Dose Epinephrine Push - 0.001mg/kg epinephrine IV bolus as required.
Karla A. Atlas of Pediatric Intubation Technique [Internet]. Pediatric Anesthesia. Digital Handbook. 2023. Available from: https://www.maskinduction.com/atlas-of-pediatric-intubation-technique.html
BCCH Pediatric Intensive Care Unit – Medical Director. INTUBATION IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS [Internet]. 2022. Available from: https://shop.healthcarebc.ca/phsa/BCWH_2/BC%20Children%27s%20Hospital/C-05-07-62873.pdf
BC Children’s Hospital. How to reconstitute a Low Dose Push Epinephrine Syringe, 10mcg/ml. 2024.
Medication
If the weight is not immediately known or easily estimated, use age on weight based drug sheets on this site or a Broselow tape can be used for the purpose of drug dosages (as well as ET tube sizing).
- Sedation, Analgesia, & Paralytics: Consider having multiple doses at the bedside for the procedure.
Ketamine 1mg/kg
Rocuronium 1mg/kg
Fentanyl 1 mcg/kg (adjunct)
If the child is hypertensive following intubation, a repeat dose of ketamine or fentanyl can be administered.